As humans, we are skilled at identifying when water isn’t clean or food is tainted just by looking at it or smelling it. However, it can be challenging to determine whether the air we breathe is safe or not. Larger pollutants are easier to spot, which isn’t the case for the smaller ones.
In this article, we will talk about the particles that are harder to detect, as well as their effect on our bodies.

What Is PM2.5?
PM2.5 are inhalable particles or droplets in the air, with a diameter of 2.5 micrometres or smaller. Hence, PM is an abbreviation for Particulate Matter, and 2.5 signifies the size of the particulate matter.
The width of the larger particles in the PM2.5 size range would be about 30 times smaller than a strand of hair. Since they are so small and invisible to the human eye, it’s no surprise that we can’t tell that we’re breathing in dangerous contaminants.
Where Does PM2.5 Come From?
Some of the most common sources of PM2.5 particles are when wood, coal, diesel fuel, oil, and gasoline are burned off, which is also known as combustion. Fine particles are also created as a reaction to gasses in the atmosphere from sources such as power plants.
Moreover, some of the fine particles are carried long distances by the wind. For this reason, volcanic eruptions and wildfires can raise fine particle concentrations hundreds of miles from their source.
PM 2.5 is also produced by activities carried out indoors. Some of these activities include burning candles, cooking such as sauteing and frying, smoking tobacco, and operating fireplaces.
It’s important to note that PM2.5 is not always created by humans. There are also natural sources of PM2.5, such as vegetation and trees that release secondary particles through chemical reactions of nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, and other gases.
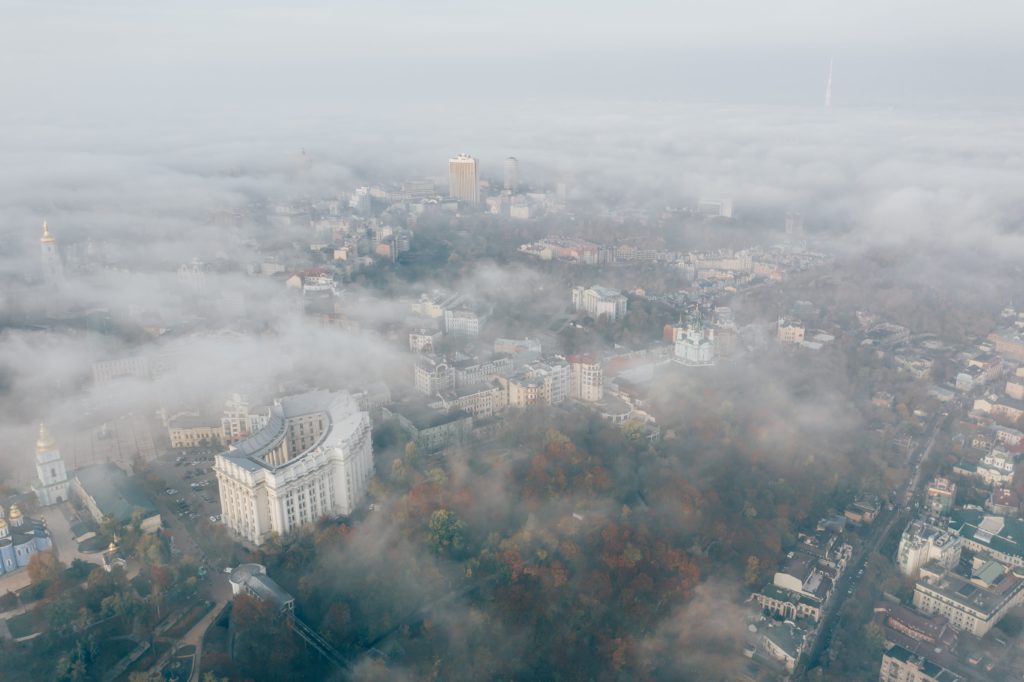
You will know that the PM2.5 levels are elevated outside when there is little to no mixing of air and wind. Generally speaking, when PM2.5 increases, there is reduced visibility and the air appears hazy, and it looks like there is fog or high humidity.
What Are the Effects of PM2.5?
When the air is polluted with PM2.5 particles, they can easily reach the deepest levels of your lungs. However, these particles don’t affect just your lungs – they also enter your bloodstream. From there, they end up harming every part of your body.
Symptoms of exposure to PM 2.5 particles include coughing, chest tightness, difficulty breathing, headaches, and irritation of the eye, nose, and throat.
The risk is especially high for people who exercise outdoors while PM2.5 levels are high since they are inhaling more deeply than other people.
Another group that is considered most at risk is children since their bronchial airways and lungs are still in development. Moreover, compared to adults, children spend more time outdoors, which means they have a higher chance of breathing in polluted air.
Lastly, people with preexisting lung and heart disease and elders are particularly sensitive to PM2.5.
Final Thoughts
When levels of PM2.5 are elevated, reduce your exposure by going indoors and limiting outdoor activities.
Even though it can be difficult to control the air pollutants outdoors, there still are a lot of ways to monitor the air quality and protect your body from the diseases and illnesses caused by airborne pollutants.
Do you want to know the quality of the air you breathe? Download AirCare – our free mobile app that tracks air pollution from your pocket, and check out the AirCare blog!